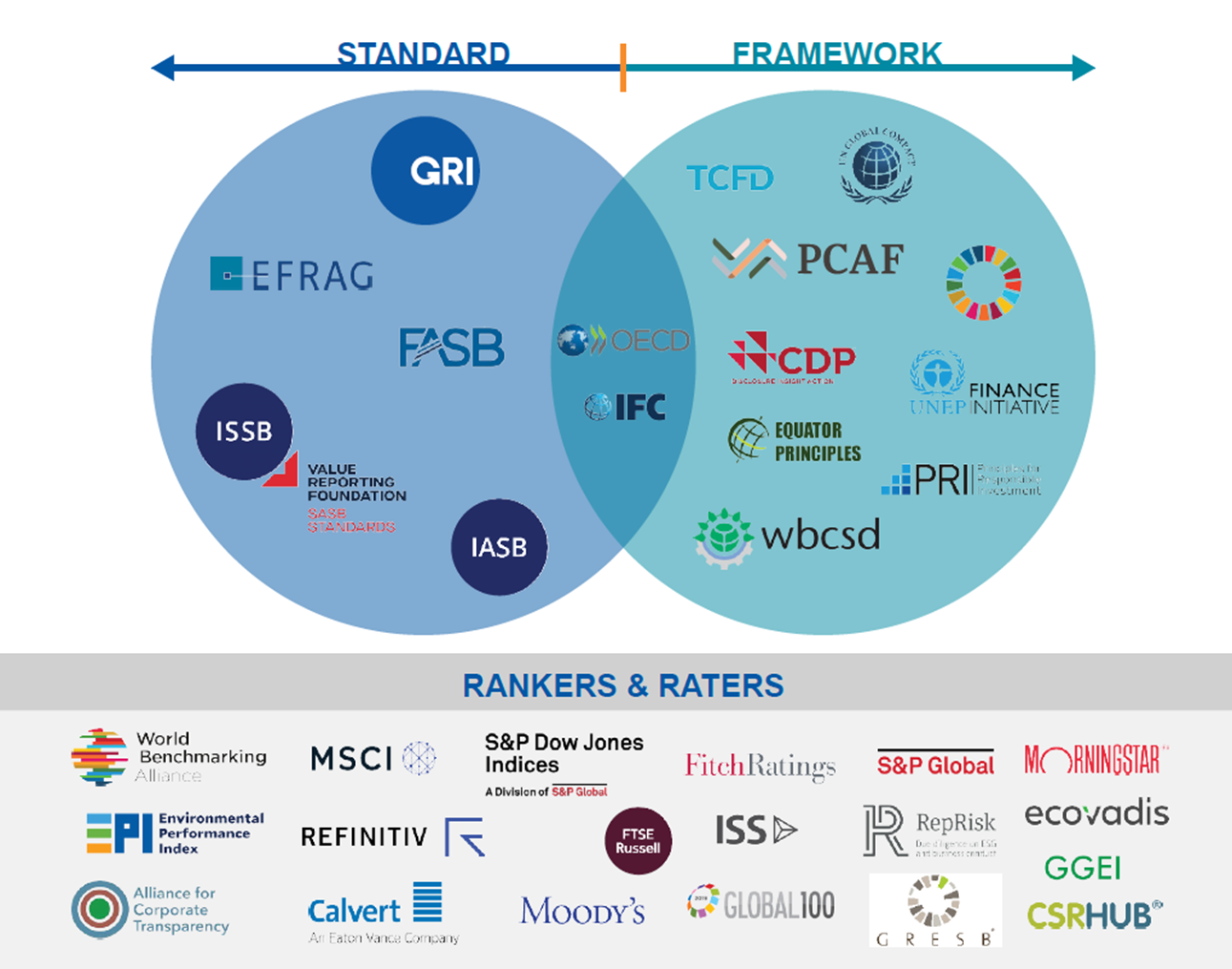
There are a ton of sustainability reporting frameworks out there, so how can companies decide which one to use? Our Trust Geek Glossary blog series is here to help clear things up. We covered CDP and SASB in the first two articles, and here we’re exploring one of the most popular ESG reporting standards – the Global Reporting Initiative, or GRI.
What’s GRI? What’s the history of the Global Reporting Initiative?
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) was founded in 1997, following public outrage over the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Still one of the largest environmental disasters of all time, it spilled 11 million gallons of oil into the Gulf of Alaska in the spring of 1989. In response, a group of socially responsible investors, environmental groups, and nonprofits came together in 1990 to form the Coalition for Environmentally Responsible Economies (Ceres). Ceres established the Valdez Principles (later renamed as the Ceres Principles), a voluntary code of conduct for companies to support the protection of the environment.
At that time, sustainability reporting was virtually unheard of – very few companies provided non-financial disclosures. Ceres founder, Joan Bavaria, realized that the principles would need to have an accountability mechanism in place to have any real impact. For the next several years, she collaborated with Dr. Allen White, the VP of Tellus Institute, to develop a reporting framework for the Ceres Principles. This became the basis for the initial GRI guidelines (G1), released in 2000, the first global framework for ESG reporting. As GRI grew, the reporting system was broadened to include a global scope and social, economic, and governance issues. And, in 2002, GRI relocated to Amsterdam as an independent global institution and collaborating center of the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP).
Today, GRI is one of the most widely-used systems available for disclosing ESG performance with more than 10,000 reporters in 100 countries.
What is GRI infographic
The infographic that follows provides a quick overview of GRI:
- Founded: 1997
- Number of companies reporting: 10k+
- Typical audience: Broad stakeholder base
- Purpose: Help organizations be transparent and take responsibility for their impacts by creating common global standards for reporting that include an independent, multi-stakeholder process.
- Focus: External environmental, societal, and economic impacts.
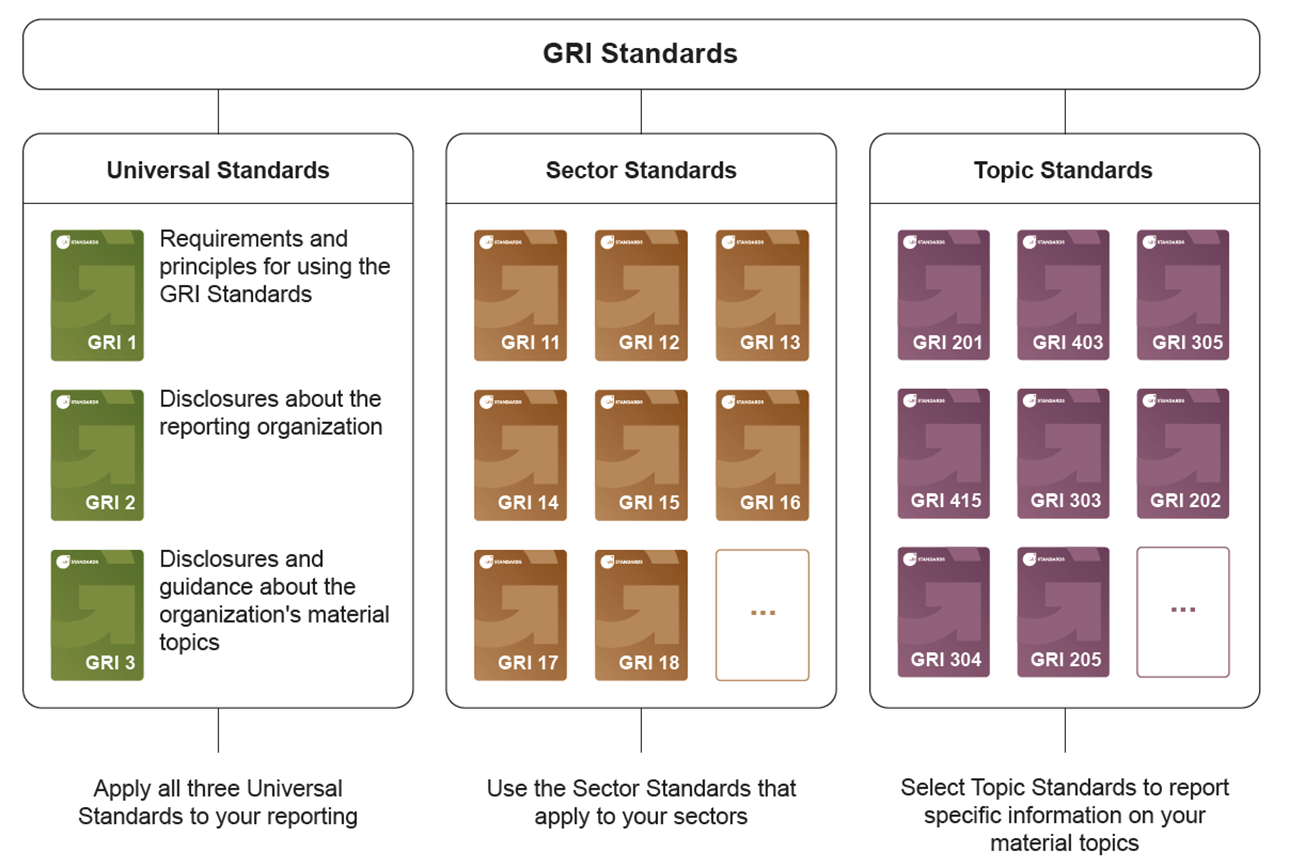
- What is reported: All three ESG pillars. General disclosures, sector-specific disclosures, and topic-specific disclosures.
- Who reports: Most large companies globally use the GRI standards.
- Industry-specific versions: 40 industry-specific standards coming, starting with high impact sectors.
- Output used for: Company’s public ESG report and other (sustainability indices, awards, etc.)